Serotonin is often called the “happy hormone,” and for good reason. It plays a vital role in regulating your mood, sleep, digestion, and more. But what exactly is serotonin—and can you increase it naturally? In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll explore the science behind serotonin and 9 simple ways to support your body’s natural production of this mood-boosting chemical.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Serotonin?
The Science Behind the “Happy Hormone”
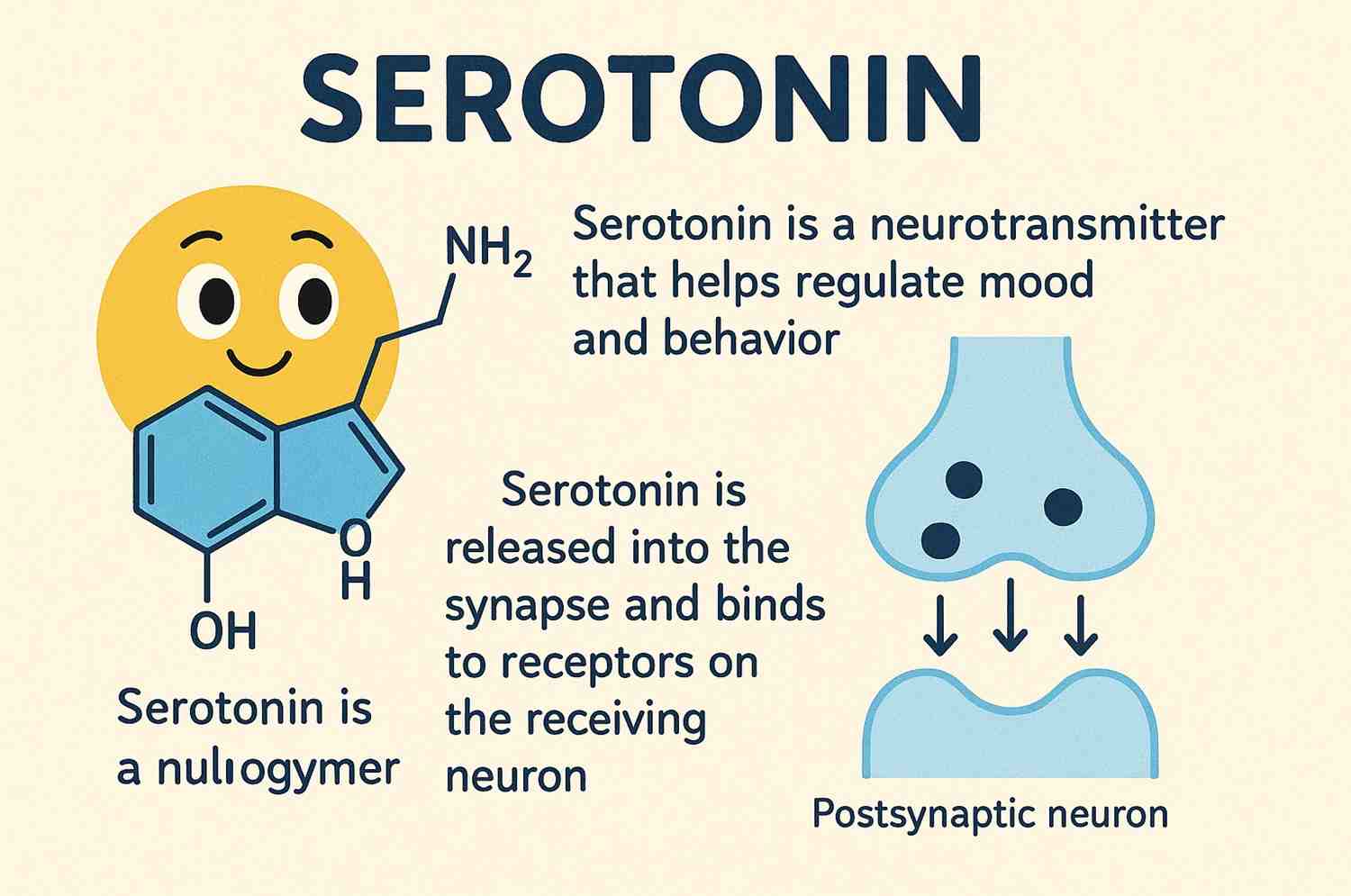
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter—a chemical messenger that helps transmit signals in the brain. It plays a vital role in stabilizing mood, feelings of well-being, and happiness, which is why it’s often nicknamed the “happy hormone.” But serotonin is more than just a mood booster. It’s involved in a range of essential body functions like regulating sleep, digestion, memory, and even sexual desire.
Chemically, serotonin is derived from tryptophan, an amino acid that enters the body through food. Once consumed, tryptophan is converted to 5-HTP (5-hydroxytryptophan) and then into serotonin through a process involving the brain and the digestive tract.
Serotonin doesn’t work in isolation—it interacts with other chemicals like dopamine and norepinephrine, affecting everything from motivation to energy levels.
Where Is Serotonin Produced? (Hint: Not Just the Brain)
Most people assume serotonin is made in the brain, but here’s the surprise: over 90% of the body’s serotonin is actually produced in the gut, specifically in the intestinal lining.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Gut (Intestines): Houses the majority of serotonin, helping regulate bowel movements and appetite.
- Brain (Central Nervous System): The serotonin produced here helps control mood, anxiety, sleep, and pain.
- Blood Platelets: Store serotonin and release it during injury to aid in blood clotting.
This strong gut-brain connection is a big reason why the gut is often called the “second brain.” When your gut health is off, your mood and mental clarity can suffer too.
How Serotonin Affects Mood, Sleep, and Digestion
Serotonin has far-reaching effects throughout the body. Here’s how it influences key areas of your health:
1. Mood Regulation
Low serotonin levels are commonly linked to depression, anxiety, and irritability. Many antidepressant medications (like SSRIs) work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain to help stabilize mood.
2. Sleep Cycles
Serotonin is a precursor to melatonin, the hormone responsible for sleep. It helps regulate your internal clock (circadian rhythm), which governs when you feel sleepy or alert.
3. Digestion and Appetite
In the gut, serotonin helps control bowel function, reduces appetite, and contributes to nausea regulation. An imbalance in serotonin may lead to issues like IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) or loss of appetite.
9 Natural Ways to Boost Your Serotonin Levels
Serotonin—often called the “feel-good” hormone—plays a vital role in mood regulation, sleep, digestion, and overall emotional well-being. While medications are available for serious imbalances, there are also natural, science-backed ways to enhance your body’s serotonin production.
Below are 9 proven lifestyle habits that can naturally elevate your serotonin levels.
1. Get Daily Sunlight Exposure
Natural sunlight helps stimulate serotonin production in the brain. Just 10–30 minutes of sunlight a day—especially in the morning—can significantly improve mood and energy levels. If you’re indoors often or live in a cloudy area, consider a light therapy box.
2. Eat Serotonin-Boosting Foods (Tryptophan-Rich Diet)
Tryptophan is an amino acid that your body uses to produce serotonin. Include foods like eggs, cheese, tofu, salmon, nuts, seeds, turkey, and bananas in your daily diet. Pairing tryptophan-rich foods with healthy carbs helps with better absorption.
3. Exercise Regularly—Even a Short Walk Helps
Exercise releases endorphins and also boosts serotonin. Aerobic workouts like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for 30 minutes a day can enhance your mood naturally. Even 10 minutes of movement can make a difference on low-energy days.
4. Practice Gratitude and Positive Thinking
Focusing on what you’re thankful for can increase serotonin activity in the brain. Try journaling 3 things you’re grateful for each day or doing short affirmations to rewire your mindset. Positivity isn’t forced—it’s a skill you can train.
5. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Poor sleep disrupts serotonin production. Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, reduce blue light exposure at night, and create a calming bedtime routine. Deep, uninterrupted sleep allows your brain to naturally regulate mood chemicals like serotonin and melatonin.
6. Try Meditation or Deep Breathing Exercises
Mindfulness practices like meditation reduce cortisol (stress hormone) and improve emotional balance. Deep breathing, yoga, or guided meditations increase serotonin by calming the nervous system and promoting mental clarity. Just 10 minutes a day can help.
7. Add Probiotics for Gut Health
Your gut produces about 90% of your body’s serotonin. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and kombucha help balance gut bacteria, which supports serotonin production. A healthy gut often equals a happier brain.
8. Engage in Meaningful Social Connections
Spending time with people who uplift you releases serotonin and oxytocin. Even brief conversations or acts of kindness can make a difference. Loneliness is a serotonin killer—connection is powerful medicine.
9. Listen to Music or Do What You Love
Joyful activities trigger the brain’s reward system. Listening to your favorite music, painting, dancing, or engaging in any hobby you love can help your brain naturally release more serotonin. Make time for passion, not just productivity.
Signs of Serotonin Deficiency
Serotonin plays a key role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and even pain perception. When levels drop too low, it can disrupt multiple areas of mental and physical health. Common signs of serotonin deficiency include:
- Persistent sadness or low mood
You may feel emotionally flat or experience frequent, unexplained crying spells. - Chronic anxiety or nervousness
A constant sense of worry or restlessness can be a sign your serotonin levels are out of balance. - Sleep problems
Difficulty falling or staying asleep, or waking up feeling unrested, may indicate a chemical imbalance. - Fatigue or low energy
Even with adequate sleep, serotonin deficiency can leave you feeling physically drained and mentally foggy. - Loss of interest in activities
A lack of pleasure in things you once enjoyed—known as anhedonia—can be linked to low serotonin. - Increased irritability or anger
You may find yourself snapping more easily or feeling on edge for no clear reason. - Cravings for carbs or sugar
The body may subconsciously try to boost serotonin by reaching for comfort foods. - Digestive issues
Since much of serotonin is produced in the gut, symptoms like bloating, constipation, or IBS may appear.
When to Talk to a Mental Health Professional
It’s normal to experience low mood occasionally, but when these symptoms persist or affect daily functioning, it’s time to seek support. Reach out to a mental health professional if you notice:
- Symptoms lasting more than two weeks
- Thoughts of self-harm or hopelessness
- Inability to complete everyday tasks
- Severe anxiety or panic attacks
- A history of depression or mood disorders in your family
Early intervention can make a huge difference. Mental health professionals can help diagnose the issue, recommend therapies, and if needed, suggest serotonin-boosting medications or lifestyle strategies. You don’t have to face this alone—support is available, and healing is possible.
Can Supplements Help Boost Serotonin?
While lifestyle changes and therapy are the gold standards for long-term mental health, certain supplements may support healthy serotonin levels—especially when used thoughtfully and under guidance. These natural compounds can assist in mood regulation, sleep, and emotional well-being, though they are not a cure-all.
Natural Supplements (e.g., 5-HTP, St. John’s Wort)
- 5-HTP (5-Hydroxytryptophan):
This supplement is derived from the seeds of the African plant Griffonia simplicifolia and is a direct precursor to serotonin. It may help ease symptoms of mild depression, anxiety, and even sleep disturbances by boosting serotonin production in the brain. - St. John’s Wort:
An herbal remedy often used in Europe for mild to moderate depression. It’s believed to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine—thereby enhancing mood naturally. - L-Tryptophan:
An amino acid found in protein-rich foods, L-tryptophan can also be taken as a supplement. It plays a role in the body’s production of serotonin and melatonin, helping with mood and sleep regulation. - SAM-e (S-Adenosyl Methionine):
A naturally occurring compound in the body that may support neurotransmitter balance, including serotonin. Some studies show it can be effective for depression, particularly in people who do not respond to traditional medications.
⚠️ Note: The effectiveness of these supplements varies widely from person to person, and not all claims are supported by strong scientific evidence.
Important Safety Note Before Using Supplements
While “natural” sounds safe, serotonin supplements can still carry risks:
- Drug Interactions: Supplements like St. John’s Wort can interfere with antidepressants, birth control pills, blood thinners, and more.
- Serotonin Syndrome Risk: Combining multiple serotonin-boosting substances (e.g., 5-HTP + SSRIs) can dangerously increase serotonin to toxic levels.
- Quality Matters: Supplements are not strictly regulated. Always choose reputable, third-party-tested brands.
- Consult a Professional: Speak with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement—especially if you’re already on medication or have underlying health conditions.
Supplements can support serotonin health but should never replace professional mental health treatment or prescribed medications
Final Thoughts: It’s About Balance, Not Perfection
At the heart of every lasting change—whether it’s improving your mental health, relationships, or daily habits—is the understanding that progress doesn’t require perfection. Life isn’t a straight line; it’s a series of ups and downs, wins and setbacks. The goal is not to eliminate every flaw or challenge but to create a more balanced, meaningful way of living. By embracing flexibility, self-compassion, and small, consistent efforts, you give yourself the freedom to grow without the burden of unrealistic expectations. Remember, the journey is just as important as the destination—and balance is what helps you stay grounded along the way
Also Read:
How to Overcome Social Anxiety: A Beginner’s Guide to Beating Social Phobia
How to Deal with Depression After a Breakup: 11 Healing Steps to Rebuild Your Life
FAQ:
1. What is serotonin and what does it do?
Serotonin is a brain chemical that regulates mood, sleep, digestion, and overall emotional well-being.
2. How can I naturally boost serotonin levels?
Exercise regularly, get sunlight, eat tryptophan-rich foods, meditate, sleep well, and practice gratitude daily.
3. Does serotonin only affect mood?
No, serotonin affects mood, sleep, digestion, appetite, memory, and even sexual function, not just mood.
4. Is serotonin the same as dopamine?
No, serotonin and dopamine are different neurotransmitters with distinct roles in mood and behavior regulation.
5. Can low serotonin cause depression?
Yes, low serotonin levels are linked to depression by affecting mood, sleep, and emotional regulation.